What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
An oven that makes sure dinner’s hot by the time you get home. A fridge that reminds you that you’re out of milk. A doorbell that lets you check who’s at the door from your phone. The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to make our lives easier and more efficient than ever before. But what do we give up when we use these devices, and are they worth the cost?
Carlos Martinez
Jul 31, 2018 · 6 min read

What is the Internet of Things?
IoT, or the Internet of Things, is an internet formed not between human users, but between interconnected devices that share data with each other. Once you embed a processor and a load of IoT sensors into a tool, machine or appliance, there are few limits to what it can do.
The concept of the IoT has been around for a while. In the 1980s, researchers at Carnegie Mellon had an internet-connected soda machine that they could check online to see if it had any drinks available before visiting it. However, interest in IoT devices has exploded. Smaller and more powerful processors and smartphone app integrations are making it possible.
Why is IoT important?
Estimates say that by 2025 there will be 75 billion connected devices worldwide. IoT not only contributes to the technological innovations and economy, but it also carries severe cybersecurity risks that must be addressed. While companies that install IoT devices are aware about their vulnerabilities, regular users still lack the basic understanding of the potential harm IoT can cause.
What are the advantages of IoT?
The Internet of Things lets us control a wide range of devices, thus changing the ways we communicate with machines. It also saves time and money as you can receive and transmit data remotely.
IoT applications and examples

Consumer electronics (smart home)
- A refrigerator that can order certain foods when you’re running low.
- A thermostat you can control to cool your apartment as you head home after a hot summer day.
- An oven that you can set to preheat from your smartphone on your way home.
Healthcare
IoT devices can remotely monitor medical equipment and patient vitals signs, send alerts to nurses, and even check the condition of prostheses.
Utilities
Water, electricity, oil and gas industries are built on heavy infrastructure that is usually spread across the country. This includes thousands of pipes, valves, and meters that need to be monitored no matter what. Fortunately, some issues can be diagnosed or even predicted and prevented remotely using IoT devices.
Transportation
One single router can allow you to track the bus' location, create a hotspot so the passengers could connect to the internet, and support a CCTV camera inside. Cars, trucks, trains, boats, even planes have IoT devices installed aboard.
Manufacturing
Large factories run like clockwork, so it’s important to control every process and monitor the equipment. Be it a sawmill, frozen food factory, or a steal producer — they can all benefit from IoT.
Retail
ATMs, point of sales systems (POS), and vending machines are driven by IoT devices providing backup internet connectivity and monitoring.
The technology behind IoT devices
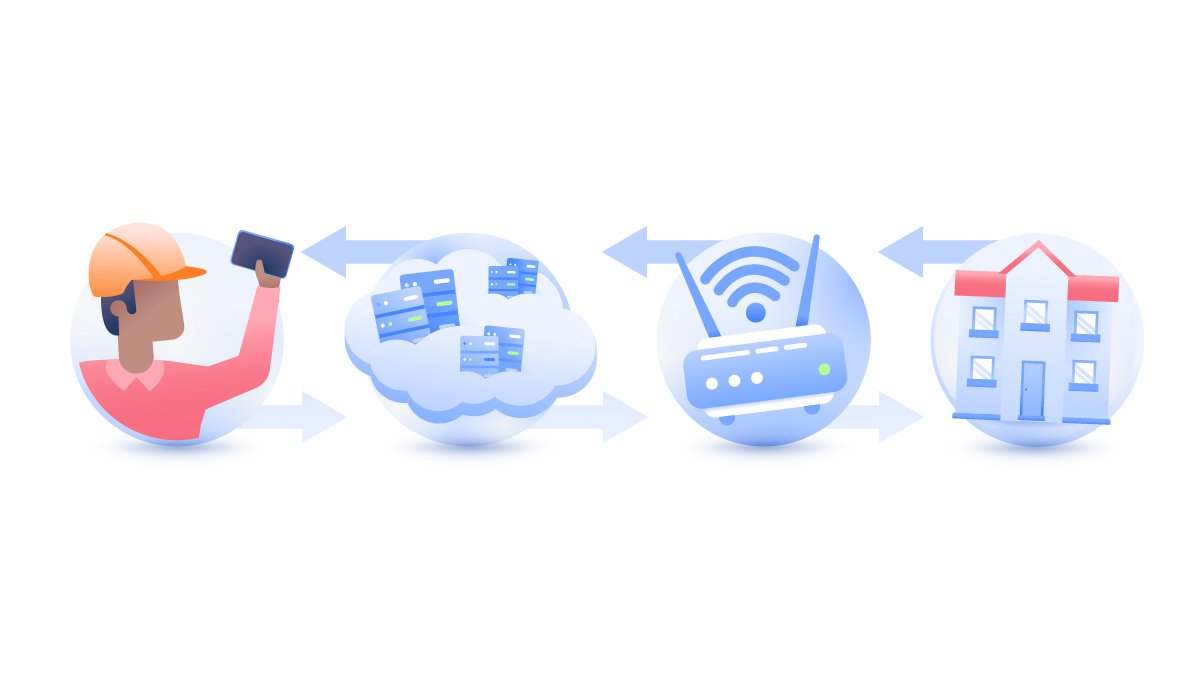
IoT devices connect to the internet via GSM cellular networks, Wi-Fi, or ethernet. Let’s say you have a smart home system that allows you to remotely control temperature, monitor your surroundings, turn off the lights, feed your dog, and lock the door with your voice. The whole system is connected to a router that collects data and sends it to various servers. You can then access that data, get alerts, and send commands through your smartphone app.
The company that installed this system can manage thousands of houses around the country. Your router belongs to the company's network and its engineers can connect to it remotely.
They use remote management systems (IoT platforms) that allow them to change passwords, send SMS notifications, fix issues, update firmware, reboot, or extract data of hundreds of routers at once. While IoT platforms are really efficient to manage a large fleet of devices, the consequences in case of cyber incident would be colossal.
IoT cybersecurity risks
Right now, IoT devices are a perfect storm of cybersecurity vulnerability. Here’s why:
- IoT security is difficult to implement. Even if manufacturers aren’t in a big hurry, security can be hard to get right on IoT devices. That’s because of the technical limitations of what they’re working with. Programming the device itself is very different from programming a program’s UI, and all of this usually has to work on potentially proprietary and low-power platforms. That means limited computing power for any sort of encryption, decryption, or other rudimentary security-oriented processes.
- Many IoT devices are shipped with default logins. Instead of giving each device a unique username and password, it’s much easier to give them default passwords and logins. Think admin//admin123. If a device even comes with instructions on how to change the password, most users probably don’t follow them. That makes it very easy for hackers to log into them – as long as they can find them. Which brings me to my next point…
- There is a search engine for IoT devices. Shodan is a search engine that lets you search the world for IoT devices. You can search by technical parameters or with simple terms like “webcam,” but both will return thousands of devices for you to browse. If it’s connected to the internet, there’s a good chance that Shodan can find it. From there, a hacker who’s done even a tiny bit of research can log in with very little effort if the device is vulnerable. If they’re a determined attacker, then even somewhat secured devices may not be safe.
- IoT devices are excellent malware hosts. Because their security is questionable, IoT devices can often be used to host and run rudimentary malware. They’re tremendously useful in DDoS attacks (click here to learn more about them), which require swarms of devices running simple bots to swamp their targets.
Even if your IoT device is totally secure, there’s another huge risk it might expose you to – privacy violations. These devices are notorious for harvesting data for their manufacturers. This data is ostensibly only used to improve their devices, but few companies will be able to resist the price that detailed user data could fetch.
The consequences of hacked IoT devices
Since Internet of Things (IoT) devices are part of huge infrastructures, the consequences in case of a hack could affect millions of people. Hackers could break into a power management system, for example, and leave an entire city without electricity.
How about the smart home industry? Imagine a stalker watching your family through your security camera or remotely unlocking your door. If your house is equipped with IoT devices, it means that somebody with the right skills can monitor your activities and exploit your home.
Even smartwatches aren’t reliable as they can trick patients into taking pills and cause health problems or even death.
How to secure your IoT devices
- RTFM and change your password. RTFM stands for “Read The Friendly Manual” (not sure I got that third word right…). If your IoT device manufacturer puts at least a bit of effort into securing your device, you should be able to change the password from the factory default to something secure. Check out our guide to creating a secure password. Make sure the password for each device is different, too. This is a small and easy change that can make a big difference, so don’t skip it.
- Ask yourself: “Do I really need to access this device remotely?” If you love the features offered by the IoT, a healthy dose of skepticism might be just what the doctor ordered. It can be hard to consider what sort of impact an IoT device might have on your life, but realizing that you’ll be fine with a WiFi-free oven is a guarantee that it’ll never be hacked!
- Create an offline WiFi LAN. If you’ve got an extra router, and if your devices can operate on a LAN, this can be a great choice for staying secure. Many people don’t realize that your router can operate without connecting to the internet. You can use it to create a local network that your home devices connect to along with the smartphone or computer you want to use to control them. Some devices can even support simultaneous connections to two WiFi networks with a bit of configuration.
- Keep your devices updated. Not all manufacturers are as dedicated to their IoT devices as they should be, but if they offer updates, it would be wrong not to take them. Updates can often fix critical security vulnerabilities, and there can be a lot of those when it comes to IoT devices!
- Get a VPN for your router. Some routers are powerful enough to support the powerful encryption that NordVPN uses to secure its users. If yours does, then NordVPN will allow outbound connections while blocking incoming ones. Your devices will still be able to send you data, but no incoming communication with them will be possible. This may be inconvenient if you want to control them remotely, but the encryption will block hackers, too. You can also check out our ‘What is a virtual private network?’ section, where a VPN is explained in more details.
Protect your IoT devices with NordVPN. Try it free for 30 days!